使用 Rails 8 提供的默认缓存 Solid Cache
2025-01-05 18:00
1. 什么是缓存
缓存是提高应用程序性能的最有效方法之一。它能让运行在适度基础设施上的网站(单个服务器和单个数据库)支持成千上万的并发用户。
Rails 提供了一套开箱即用的缓存功能,不仅可以缓存数据,还可以解决缓存过期、缓存依赖和缓存失效等难题。
1.1 什么是Solid Cache
Solid Cache 利用现代 SSD(固态硬盘Solid State Drive)的速度,以更大的存储容量和简化的基础设施提供经济高效的缓存。虽然固态硬盘的速度略低于内存,但对于大多数应用来说,两者的差距微乎其微。固态硬盘可以存储更多数据,因此无需频繁失效缓存,从而弥补了这一不足。因此,缓存平均缺失次数较少,响应时间较快。默认情况下,Action Controller 缓存仅在生产环境中启用。
1.2 开始使用
接上篇使用 Rails 8 提供的默认任务队列 Solid Queue 我们还是在开发环境“手动设置为生产环境”。
export RAILS_ENV=production
让开发环境和生产环境保持一致,不失为一种”简单“做法。
接上一篇,以solid-cable分支为基础,创建一个solid-cache分支:
https://github.com/memorycancel/rails-solid/tree/solid-cache
2. 缓存种类
2.1 片段缓存
这里的片段,狭义上之HTML片段,将需要耗时渲染的HTML片段放进缓存,提升页面渲染速度。 例如缓存每篇post,修改views/posts/index.html.erb,给<%= render post %>包上一层"cache":
<% cache post do %>
<%= render post %>
<% end %>
数据库中会插入一条键为production:views/posts/index:811a75149251ed076ff1b8668f838a86/posts/1的条目。 key_hash是根据HTML片段计算的摘要,当内容不发生改变,摘要相同,直接渲染value,否则更新value和key_hash。 当删除post条目时,cache数据库不会立马删除该缓存,而是根据config/cache.yml里的max_age配置定期清除。
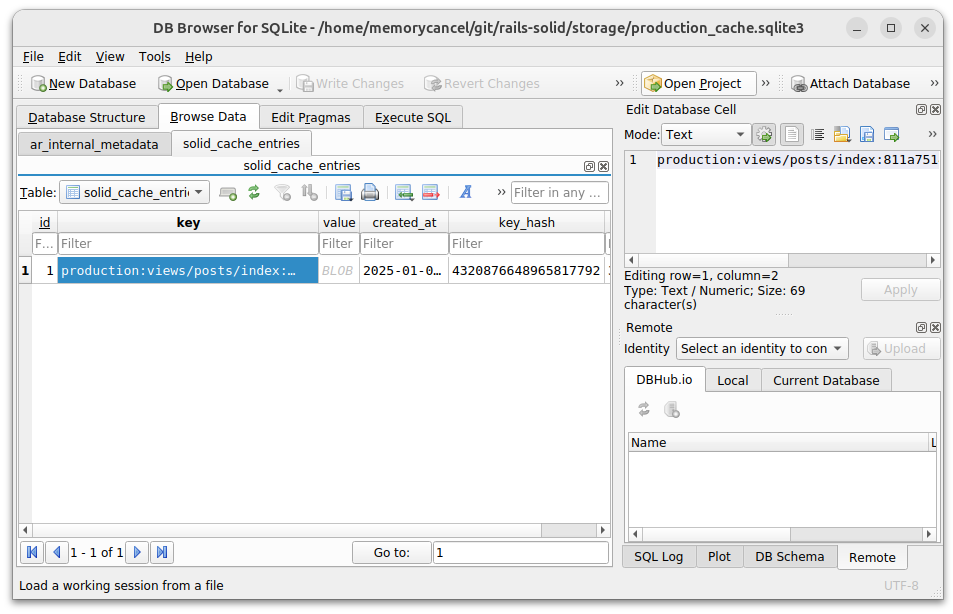
如果想在特定条件下缓存片段,可以使用 cache_if 或 cache_unless :
<% cache_if admin?, product do %>
<%= render product %>
<% end %>
2.2 集合缓存
在render helper增加 cached: true选项可以缓存集合,例如在comments/_comments.html.erb页面缓存comments集合, 将简化写法<%= render post.comments %>扩展为:
<%= render partial: 'comments/comment', collection: post.comments, cached: true %>
目前有2条comment,那么此时 cache 数据库将添加两条comment的缓存。
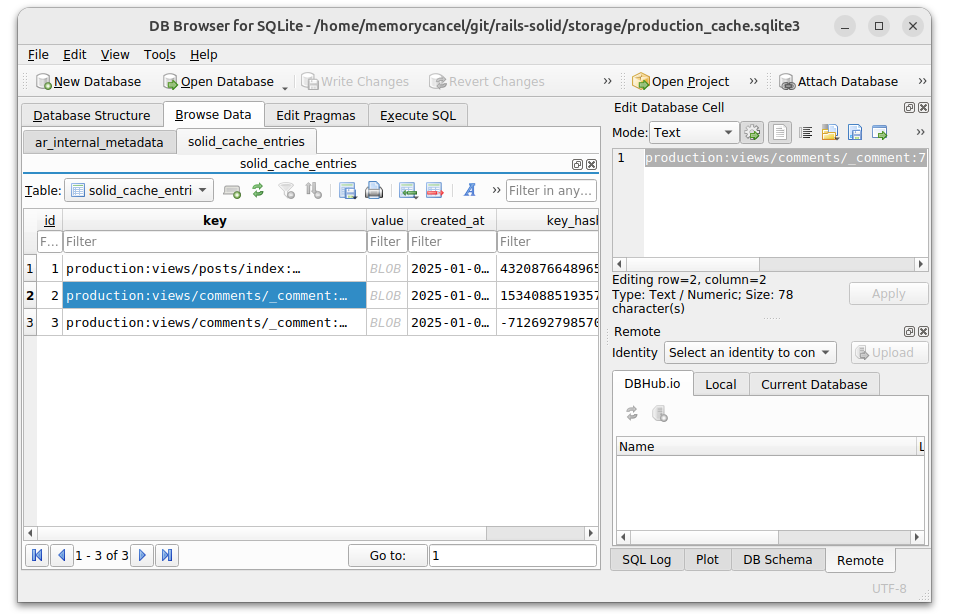
另外,缓存还能配置本地化(locale),不同的语言渲染不同的版本:
<%= render partial: 'comments/comment',
collection: post.comments,
cached: ->(comment) {[I18n.locale, comment] } %>
2.3 嵌套缓存
刚刚给comments/commentpatial添加了缓存,下面在调用此patial的地方包一层缓存:
<% cache @post do %>
<%= render "comments/comments", post: @post %>
<% end %>
此外,comment和post是从属关系,还需要添加一个 comment.rb 的选项:
belongs_to :post, touch: true
当 touch 设置为 true 时,任何更改post记录 updated_at 的操作也会更改相关comment的 updated_at ,从而使缓存过期。
2.4 低级缓存
有时需要缓存特定值或查询结果,而不是缓存HTML片段。Rails 的缓存机制非常适合存储任何可序列化的信息。 简而言之,可以当他是 key-value 数据库。
Rails.cache.write("greeting", "Hello, world!")
greeting = Rails.cache.read("greeting")
puts greeting # Output: Hello, world!
# Delete a value from the cache
Rails.cache.delete("greeting")
# Fetch a value with a block to set a default if it doesn’t exist
welcome_message = Rails.cache.fetch("welcome_message") { "Welcome to Rails!" }
puts welcome_message # Output: Welcome to Rails!
2.5 SQL缓存
SQL查询缓存是 Rails 的一项自动(隐式)功能,可缓存每次查询返回的结果集。如果 Rails 在该请求中再次遇到相同的查询,它将使用缓存的结果集,而不是再次对数据库运行查询。 第二次针对数据库运行相同的查询时,实际上并不会访问数据库。第一次查询返回的结果存储在查询缓存(内存中),第二次则从内存中提取。不过,每次检索仍会实例化所查询对象的新实例。
def index
@posts = Post.all
@posts2 = Post.all
end
例如上面只会访问数据库一次。
3 管理render依赖关系
3.1 内部依赖
大多数模板依赖关系都可以从render 调用中推导出来。下面是一些 ActionView::Digestor 解码示例:
render partial: "comments/comment", collection: commentable.comments
render "comments/comments"
render "comments/comments"
render("comments/comments")
render "header" # translates to render("comments/header")
render(@topic) # translates to render("topics/topic")
render(topics) # translates to render("topics/topic")
render(message.topics) # translates to render("topics/topic")
为了使缓存正常工作,需要显示的声明好依赖关系。
例如,不能写:
<%= render 'comments/comment',post.comments, cached: true %>
而应该写:
<%= render partial: 'comments/comment', collection: post.comments, cached: true %>
3.2 外部依赖
如果您在缓存块中使用了helper方法,然后更新了helper方法,就必须同时更新缓存。具体方法并不重要,但模板文件的 MD5 必须更改。一种建议是在helper文件中添加注释,如:
<%# Helper Dependency Updated: Jul 28, 2015 at 7pm %>
<%= some_helper_method(post) %>
4 数据库设置
4.1 基本配置位置
- config/database.yml
- config/environments/production.rb(
config.cache_store = :solid_cache_store) - config/cache.yml
4.2 缓存自动收缩任务
Solid Cache 每次写一条,id自增1。当计数器达到 “缓存 “配置中 expiry_batch_size (id条数)的 50%时,将触发一个后台任务来处理缓存过期问题。当缓存需要收缩时,这种方法可确保缓存记录的过期速度快于其写入速度。
后台任务只在有写入时运行,因此在缓存没有更新时,进程会处于空闲状态。如果希望在后台任务而不是线程中运行到期进程,请将缓存配置中的 expiry_method 设置为 :job 。
生产环境必须设置expiry_method: :job 这样任务才会存进任务队列数据库,线程停止了也不会丢失任务,从而保证可靠性。
4.3 缓存分片
Solid Cache 支持分片 - 在多个数据库中分割缓存。这将分散负载,使缓存性能更加强大。通过配置 database.yml:
production:
cache_shard1:
database: cache1_production
host: cache1-db
cache_shard2:
database: cache2_production
host: cache2-db
cache_shard3:
database: cache3_production
host: cache3-db
config/cache.yml:
production:
databases: [cache_shard1, cache_shard2, cache_shard3]
4.4 加密
缓存也可以加密,配合数据库中的条目加密https://guides.rubyonrails.org/active_record_encryption.html:
production:
encrypt: true
关于其他的缓存数据库参考:https://guides.rubyonrails.org/caching_with_rails.html#other-cache-stores
5 自定义缓存键
# This is a legal cache key
Rails.cache.read(site: "mysite", owners: [owner_1, owner_2])
6 使用 Etag
参考https://guides.rubyonrails.org/caching_with_rails.html#conditional-get-support
请谨慎使用etag,因为除非强制清除浏览器缓存,否则浏览器/代理服务器无法使缓存响应失效。